Understanding How Blockchain Works, Where It’s Used, and What’s Coming Next
Blockchain is a technology that acts like a digital ledger (A ledger is like a financial diary where you record all your money-related activities. It keeps track of your income, expenses, and other transactions in an organized way. It helps you see where your money is coming from and where it’s going, making it easier to manage and understand your finances.) or record-keeping system. Imagine a notebook that multiple people can write in, and every entry is connected to the one before it, forming a chain of information. Here’s a simple breakdown:
(Understanding How Blockchain Works, Where It’s Used, and What’s Coming Next)
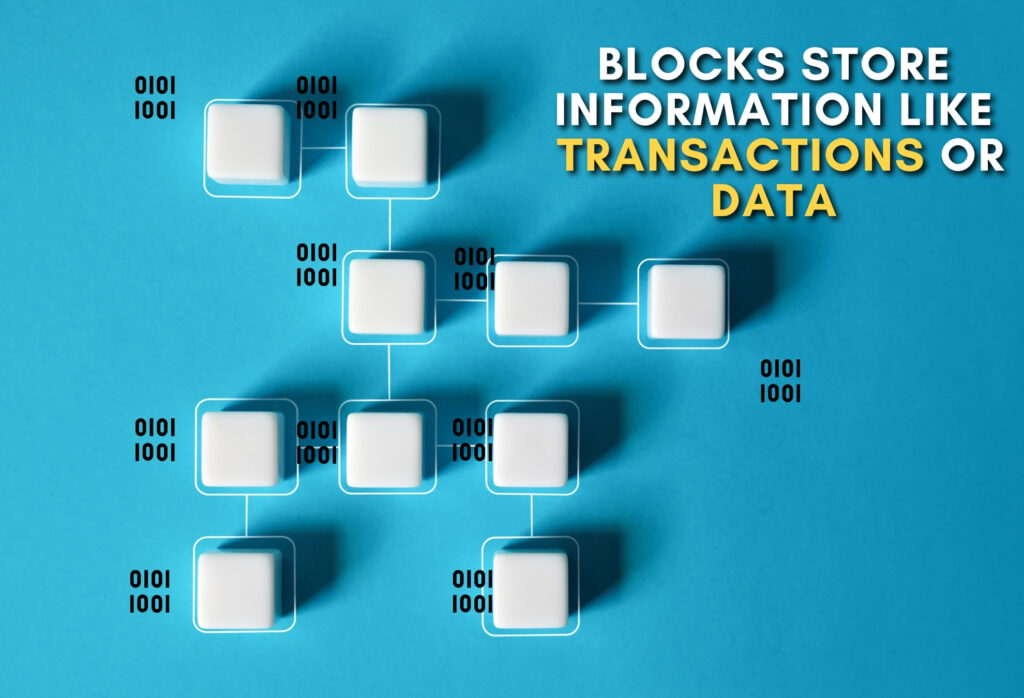
- Blocks: Each piece of information (like a page in the notebook) is a block. These blocks contain data like transactions, ownership details, or any other digital information.
- Chain: Every block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain. This linking is done using complex mathematical algorithms.
- Decentralized: Unlike a traditional ledger controlled by a single authority (like a bank), a blockchain is decentralized. It’s maintained by a network of computers (nodes) all over the world.
- Security: The linking of blocks using cryptography makes it extremely secure. Once a block is added, it’s difficult to alter previous blocks without changing every subsequent block, which is practically impossible.
Now, let’s look at a simple example:
Scenario: You want to send money to a friend using a blockchain-based cryptocurrency like Bitcoin.
- Transaction: Your transaction is broadcaster to the network. This transaction is put into a block.
- Verification: The network of computers verifies your transaction. They ensure you have the funds to make the transaction, and it’s a legitimate request.
- Block Formation: Once verified, your transaction is combined with others to create a new block.
- Adding to the Chain: This block is then added to the existing chain of blocks, and the information is now a permanent part of the blockchain.
- Decentralization: The blockchain is maintained by many computers globally, not controlled by a single entity.
The benefit? It provides a transparent, secure, and decentralized way of handling digital transactions. Blockchain technology is not limited to cryptocurrencies; it has applications in various fields like supply chain management, voting systems, and more.
Know everything related to blockchain
Introduction to Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary way of keeping digital records that’s both secure and transparent. Picture a chain of digital blocks, each containing a list of transactions or data, and these blocks are linked together, forming an unchangeable and decentralized ledger. Here’s how it works:
– Blocks and Chains: Information is grouped into blocks, and once full, they’re linked in a chain, creating the blockchain.
– Decentralization: Unlike traditional systems, blockchain isn’t controlled by a single entity. Copies of the blockchain are stored on many computers worldwide, ensuring security.
– Security with Cryptography: Each block has a unique fingerprint called a hash, and they’re linked together, making tampering nearly impossible.
– Consensus: Before a new block is added, the network agrees it’s valid through a consensus mechanism, ensuring accuracy.
– Smart Contracts: Blockchain can execute self-executing contracts known as smart contracts, automating processes when conditions are met.
– Applications: Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is explored for secure record-keeping, like tracking product origins or ensuring data integrity.
In essence, blockchain is a digital ledger providing a secure and transparent way to handle information, free from the control of a single authority. It’s like a group-shared, tamper-resistant notebook, making it a trustworthy solution for various digital transactions and record-keeping needs.
Read – What is Bitcoin Halving ?
Fundamental principles of Blockchain

The fundamental principles of blockchain are its key building blocks that make it a secure and decentralized technology. Let’s break down these principles:
- Consensus Mechanism:
– Before a new block is added to the blockchain, there needs to be an agreement among the network participants that it’s valid.
– This agreement is achieved through a consensus mechanism, ensuring that the majority of the network verifies and accepts the new information.
- Immutability:
– Once information is added to the blockchain, it’s nearly impossible to alter or delete.
– The interconnected nature of blocks, the cryptographic security, and the consensus mechanism contribute to the immutability of the blockchain.
- Smart Contracts:
– Blockchain can incorporate self-executing contracts called smart contracts.
– These are programmable contracts with predefined rules. When conditions specified in the smart contract are met, the contract executes automatically.
- Transparency:
– Every participant in the blockchain network has access to the entire history of transactions.
– All transactions are visible and verifiable by anyone in the network, enhancing transparency and trust.
- Incentives and Cryptoeconomics:
– Blockchain networks often involve incentives to encourage participants to act in the best interest of the network.
– Cryptoeconomics refers to the economic systems built into the blockchain, like rewarding participants with cryptocurrency (like Bitcoin) for validating transactions.
- Permissioned and Permissionless Blockchains:
– Blockchain networks can be either permissioned or permissionless.
– Permissionless blockchains, like Bitcoin, allow anyone to participate without needing approval. Permissioned blockchains, on the other hand, have restrictions on who can join, providing more control.
Concept of Decentralized and Distributed ledgers.

Understanding Decentralized and Distributed Ledgers in Simple Terms:
Imagine keeping track of important information with your friends, but instead of one person holding the master list, everyone has a copy. That’s the basic idea behind decentralized and distributed ledgers – a fancy way of saying we’re sharing and updating information together.
Decentralized Ledger:
In a decentralized ledger, no single person is in charge. It’s like having a group chat where everyone can add or change information. Each member has their own copy of the ledger, and whenever something new is added, everyone gets updated. This makes it secure because even if one person’s copy gets messed up, the rest of the group still has the correct info.
Distributed Ledger:
Now, think of a distributed ledger like a potluck dinner where everyone brings a dish. In a distributed ledger, the information is spread out among different places or nodes. Each node has its own piece of the ledger, and they work together to keep it accurate. If one node isn’t available, the others still have the complete story. It’s like teamwork for keeping our records safe.
Key Takeaways:
– Decentralized: Everyone has their own copy, and no one’s the boss.
– Distributed: Information is spread out among different places or nodes, working together like a team.
– Both make our record-keeping more secure, transparent, and reliable, whether we’re tracking money, votes, or anything important.
Role of cryptography in securing transactions on the blockchain.

Ever sent a secret message using a code only you and your friend understand? Well, cryptography is a bit like that, but for making sure our online transactions are super safe on the blockchain.
1. Secret Handshakes – Encryption:
– Imagine you have a magical box (that’s encryption). Before sending anything, you put your message in the box and lock it with a special key.
– Only the person with the matching key (your friend) can open and read it. This way, even if someone tries to peek, they can’t understand the message without the right key.
2. Digital Signatures – Your Unique Stamp:
– When you want to say, Yes, I agree to this transaction, you use a digital signature. It’s like your unique stamp.
– This signature is created with a secret code only you know, proving it’s really you who approved the deal. If someone tries to fake it, the system can tell it’s not your stamp.
3. Fingerprinting Blocks – Hashing:
– Each block in the blockchain has a special fingerprint called a hash. It’s like a digital ID card for the block.
– If someone tries to sneak in and change something in the block, the fingerprint (hash) would instantly change too. So, everyone can see if anything fishy is going on.
4. Public and Private Keys – Lock and Key System:
– Imagine having two keys – one to lock your magical box (public key) and another to open it (private key).
– You share the public key with the world so they can send you encrypted messages, but only you, with the private key, can unlock and read them. It’s like having a personal mailbox no one else can open.
Cryptography on the blockchain is like a super-secret language that keeps our transactions safe. It uses codes, unique stamps, digital fingerprints, and a lock-and-key system to make sure only the right people can access and understand what’s happening. It’s like having a superhero shield for your digital money!
Key Components of Blockchain:

– Explore the concept of blocks and how they are linked together.
– Discuss the role of consensus algorithms in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain.
– Explain the significance of smart contracts in automating and enforcing agreements.
Use Cases and Applications of Blockchain:
– Highlight real-world applications of blockchain technology, such as cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin), supply chain management, and healthcare.
– Discuss the potential impact of blockchain on various industries, including finance, logistics, and governance.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain:
– Address scalability issues and energy consumption concerns associated with certain blockchain networks.
– Explore the regulatory challenges and legal considerations surrounding blockchain technology.
– Discuss potential security risks and vulnerabilities in blockchain systems.
Emerging Trends and Future Developments:

– Explore the evolution of blockchain technology over time.
– Discuss emerging trends, such as the integration of blockchain with other technologies like AI and IoT.
– Speculate on potential future developments and innovations in the blockchain space.
By covering these subtopics, you can provide a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology in your blog.
Check more Blogs Related to blockchain, Crypto, bitcoin and many More.











 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  Solana
Solana  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  USDC
USDC  XRP
XRP  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Toncoin
Toncoin  Cardano
Cardano  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  Avalanche
Avalanche  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  TRON
TRON  Chainlink
Chainlink  Uniswap
Uniswap  Polkadot
Polkadot  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol  Litecoin
Litecoin  Polygon
Polygon  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  LEO Token
LEO Token  Dai
Dai  Pepe
Pepe  Internet Computer
Internet Computer  Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic  Fetch.ai
Fetch.ai  Renzo Restaked ETH
Renzo Restaked ETH  Aptos
Aptos  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Monero
Monero  Render
Render  Hedera
Hedera  Filecoin
Filecoin  Mantle
Mantle  Stellar
Stellar  Stacks
Stacks  Cosmos Hub
Cosmos Hub  OKB
OKB  Cronos
Cronos  Arbitrum
Arbitrum  Immutable
Immutable  First Digital USD
First Digital USD  dogwifhat
dogwifhat  Injective
Injective  Sui
Sui  The Graph
The Graph